Master These 5 Design Patterns and Level Up Your Engineering Skills
The patterns that separate junior developers from senior engineers
Preparing for System Design Interviews? Join ByteByteGo now for a structured preparation. They are also offering a rare 50% discount now on their lifetime plan.
Three years ago, I was writing code that worked but was impossible to maintain. Functions stretched over 200 lines, classes did everything, and adding new features meant rewriting half the application.
Then I discovered design patterns.
Not the academic theory you find in textbooks, but the practical patterns that every senior developer uses instinctively. These aren’t just interview talking points, they’re the building blocks of maintainable, scalable software.
Today, I’m sharing the 5 patterns that transformed how I write code and think about software architecture. Master these, and you’ll never look at code the same way again.
📣Frontend Masters (Sponsored)
FrontendMasters.com is one of the most recommended place to learn frontend end skills. They have high quality courses on Algorithms, JavaScript, React, TypeScript, and Node.js and they are now offering $100 off on their subscription which is quite rare.
If you always wanted to join frontend masters but couldn’t join now is the time but hurry up sale ends in 6 days, on 18th September.
Why Design Patterns Matter More Than Ever?
Before diving into the patterns, let’s address the elephant in the room: “Aren’t design patterns just over-engineering?”
Here’s the reality from working at scale:
Netflix uses the Observer pattern for its entire recommendation system
Uber built their surge pricing with the Strategy pattern
Spotify playlist system relies heavily on Factory patterns
Amazon’s shopping cart uses the Command pattern for undo operations
These aren’t academic exercises. They’re proven solutions to recurring problems that every developer faces.
Pattern #1: Observer Pattern - The Event Notification System
What It Solves
Ever needed to update multiple parts of your application when something changes? Without the Observer pattern, you end up with tightly coupled code that’s impossible to maintain.
How It Works
The Observer pattern defines a one-to-many dependency between objects. When one object changes state, all dependents are automatically notified.
Real-World Example
Think of YouTube subscriptions. When a creator uploads a video:
Subscribers get notifications
Recommendation algorithm updates
The analytics system logs the event
CDN starts caching the new content
All these systems “observe” the upload event without knowing about each other.
Code Impact
Before Observer Pattern:
// Nightmare code - everything coupled
function uploadVideo(video) {
saveVideo(video);
sendNotificationToSubscribers(video); // Coupled!
updateRecommendations(video); // Coupled!
logAnalytics(video); // Coupled!
cacheContent(video); // Coupled!
}After Observer Pattern:
// Clean, decoupled code
class VideoUpload {
constructor() {
this.observers = [];
}
addObserver(observer) {
this.observers.push(observer);
}
upload(video) {
this.saveVideo(video);
this.notifyObservers(video); // Clean separation!
}
}Why Senior Engineers Love It
Loose coupling: Components don’t know about each other
Easy testing: Mock observers for unit tests
Scalable: Add new features without touching existing code
Event-driven: Perfect for modern reactive architectures
Pattern #2: Strategy Pattern - The Algorithm Switcher
What It Solves
Hard-coded algorithms that change based on conditions create unmaintainable if-else chains. Strategy pattern lets you swap algorithms at runtime.
Real-World Example
Uber’s pricing algorithm:
Normal pricing during regular hours
Surge pricing during high demand
Pool pricing for shared rides
Premium pricing for luxury vehicles
Same calculation interface, different strategies.
Code Impact
Before Strategy Pattern:
// Brittle pricing logic
function calculatePrice(rideType, demand) {
if (rideType === ‘pool’ && demand === ‘low’) {
// Pool calculation logic
} else if (rideType === ‘premium’ && demand === ‘high’) {
// Surge premium logic
} else if (rideType === ‘normal’ && demand === ‘medium’) {
// Normal calculation
}
// 20 more conditions...
}After Strategy Pattern:
// Clean, extensible pricing
class PricingContext {
constructor(strategy) {
this.strategy = strategy;
}
calculatePrice(rideData) {
return this.strategy.calculate(rideData);
}
}
// Easy to add new strategies
const surgeStrategy = new SurgePricingStrategy();
const pricing = new PricingContext(surgeStrategy);Business Impact
A/B testing: Swap algorithms without deployment
Regional customization: Different strategies per market
Performance optimization: Choose the fastest algorithm per context
Pattern #3: Factory Pattern - The Object Creator
What It Solves
Creating objects with complex initialization logic scattered throughout your codebase leads to duplication and maintenance nightmares.
Real-World Example
Database connection creation:
MySQL connections for user data
Redis connections for caching
PostgreSQL for analytics
MongoDB for content storage
Each needs a different configuration, but the interface remains consistent.
Code Impact
Before Factory Pattern:
// Object creation chaos
function getUserData() {
const mysqlConfig = { host: ‘user-db’, port: 3306, ssl: true };
const connection = new MySQLConnection(mysqlConfig);
// 20 lines of MySQL-specific setup
return connection;
}
function getCacheData() {
const redisConfig = { cluster: true, nodes: [’redis1’, ‘redis2’] };
const connection = new RedisConnection(redisConfig);
// 15 lines of Redis-specific setup
return connection;
}After Factory Pattern:
// Clean object creation
class DatabaseFactory {
static createConnection(type) {
switch(type) {
case ‘user’: return new MySQLConnection(userConfig);
case ‘cache’: return new RedisConnection(cacheConfig);
case ‘analytics’: return new PostgreSQLConnection(analyticsConfig);
}
}
}
// Simple, consistent usage
const userDB = DatabaseFactory.createConnection(’user’);Why It’s Essential
Consistency: Same interface for different implementations
Testing: Easy to mock different database types
Configuration: Centralized setup logic
Flexibility: Add new database types without touching existing code
Pattern #4: Command Pattern - The Action Encapsulator
What It Solves
When you need to queue, log, or undo operations, mixing business logic with execution logic creates messy code.
Real-World Example
Text editor operations:
Type text
Delete characters
Format text
Insert images
Each action needs to be undoable, redoable, and loggable.
Code Impact
Before Command Pattern:
// Undo/redo nightmare
class TextEditor {
type(text) {
this.content += text;
this.history.push({action: ‘type’, text: text}); // Manual tracking
}
delete() {
this.content = this.content.slice(0, -1);
this.history.push({action: ‘delete’}); // Manual tracking
}
undo() {
// 50 lines of complex undo logic for each action type
}
}After Command Pattern:
// Clean, extensible operations
class TypeCommand {
execute(editor) {
editor.addText(this.text);
}
undo(editor) {
editor.removeText(this.text.length);
}
}
class CommandManager {
execute(command) {
command.execute(this.editor);
this.history.push(command); // Automatic tracking
}
undo() {
const command = this.history.pop();
command.undo(this.editor); // Automatic undo
}
}Enterprise Applications
Payment processing: Queue, retry, and rollback transactions
Workflow systems: Track and replay business processes
Audit logs: Every action is automatically logged
Macro recording: Batch operations for productivity tools
Pattern #5: Singleton Pattern - The One and Only
What It Solves
Some objects should only exist once in your application — database connections, configuration managers, and logging services. Multiple instances create chaos.
Real-World Example
Application configuration:
Database URLs
API keys
Feature flags
Environment settings
You want one source of truth, accessible globally.
Code Impact
Before Singleton Pattern:
// Configuration chaos
function getUserService() {
const config = new Config(); // New instance every time!
config.load(’database.yml’);
return new UserService(config);
}
function getOrderService() {
const config = new Config(); // Different instance!
config.load(’database.yml’); // Reloading same file
return new OrderService(config);
}After Singleton Pattern:
// One configuration, everywhere
class Config {
static instance = null;
static getInstance() {
if (!Config.instance) {
Config.instance = new Config();
Config.instance.load();
}
return Config.instance;
}
}
// Clean usage everywhere
const config = Config.getInstance();
const userService = new UserService(config);Modern Applications
Logger instances: One logger, consistent formatting
Cache managers: Single Redis connection pool
Feature flags: One configuration source
Authentication: Single JWT validator
How These Patterns Work Together
The magic happens when patterns combine. Here’s how Netflix might use all 5:
Singleton: Configuration manager for database URLs and API keys
Factory: Create different types of content processors (video, audio, subtitles)
Strategy: Different recommendation algorithms per user segment
Command: User actions (play, pause, add to list) for analytics
Observer: Notify multiple systems when the user watches content
This isn’t theoretical — this is how production systems actually work.
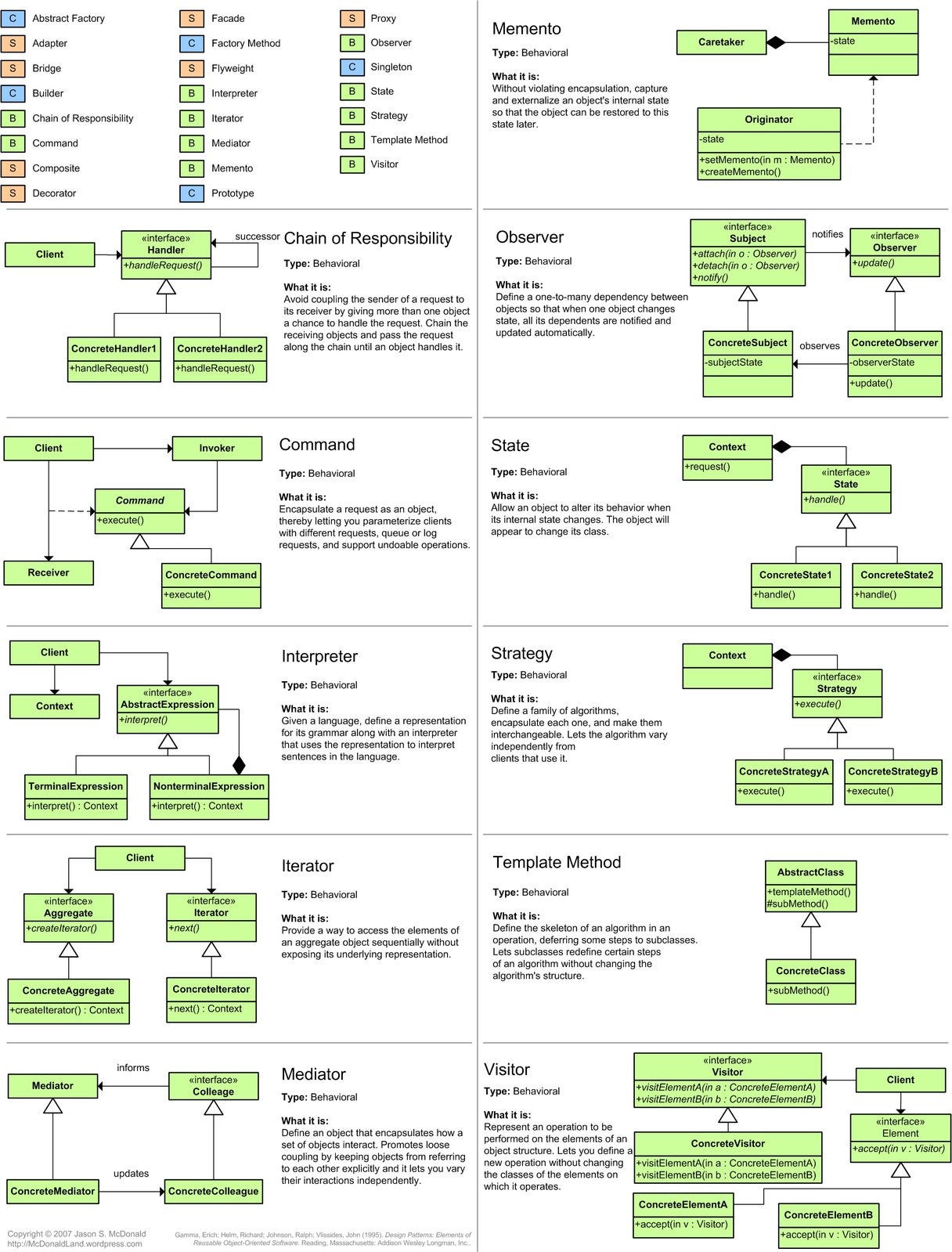
Also, here is a nice cheat sheet of all the object-oriented patterns you can learn
Final Thoughts
Design patterns aren’t just coding techniques — they’re a shared vocabulary for software professionals. When you master these patterns, you:
Communicate more effectively with senior developers
Design better systems from the ground up
Debug faster by recognizing common structures
Interview confidently, knowing you speak the language
The developers who advance fastest aren’t necessarily the ones who know the most frameworks. They’re the ones who understand the underlying patterns that make all frameworks possible.
Start with Observer and Strategy patterns this week. Build something small that uses both—experience how they alter your perspective on code structure.
In 6 months, you’ll wonder how you ever built software without them.
Preparing for System Design Interviews? Join ByteByteGo now for a structured preparation. They are also offering a rare 50% discount now on their lifetime plan.