10 Database Scaling Secrets That Separate Junior from Senior Developers
Architecting for Scale: The Top 10 Database Techniques That Matter Most.
Preparing for System Design Interviews? Join ByteByteGo now for a more structured preparation. They are also offering a rare 50% discount now on their lifetime plan.
Hello folks, Database is an important component of many software architecture and that’s what also makes it one of the most important topics on System Design interviews.
But apart from interview, its also an important topic or concept for senior developers, tech lead and software architects to master and that’s what you will learn in this article.
As your application grows, database performance often becomes the bottleneck. Slow queries, timeouts, and server overloads can hurt your user experience and limit your scalability.
The good news? There are proven techniques that help you scale your database architecture — both vertically and horizontally — so it can handle growing data volumes and traffic loads efficiently.
Whether you’re building a large SaaS platform, a high-frequency trading app, or a data-heavy analytics system, these 10 database scaling techniques will help you stay ahead of performance issues.
So what are we waiting for, let’ jump into these 10 database scaling techniques every senior developer should know
10 Database Scaling Techniques Every Software Engineer Should Learn
Here are the 10 basic and advanced database scaling techniques which every senior developer should know. If you have used database in your application the there is a good chance that you already familiar with many of them but its also good to revise them before interviews.
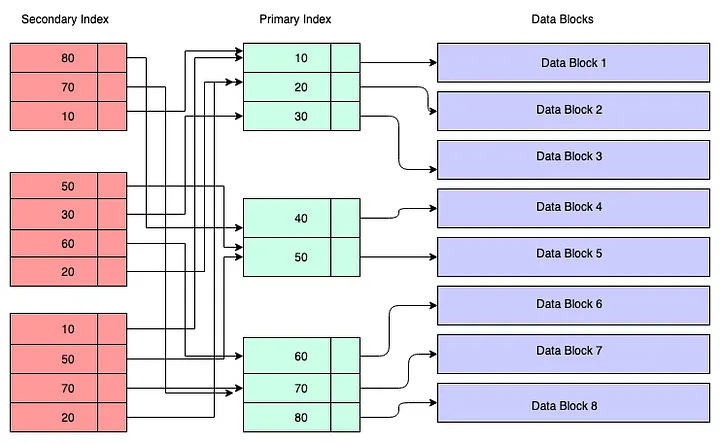
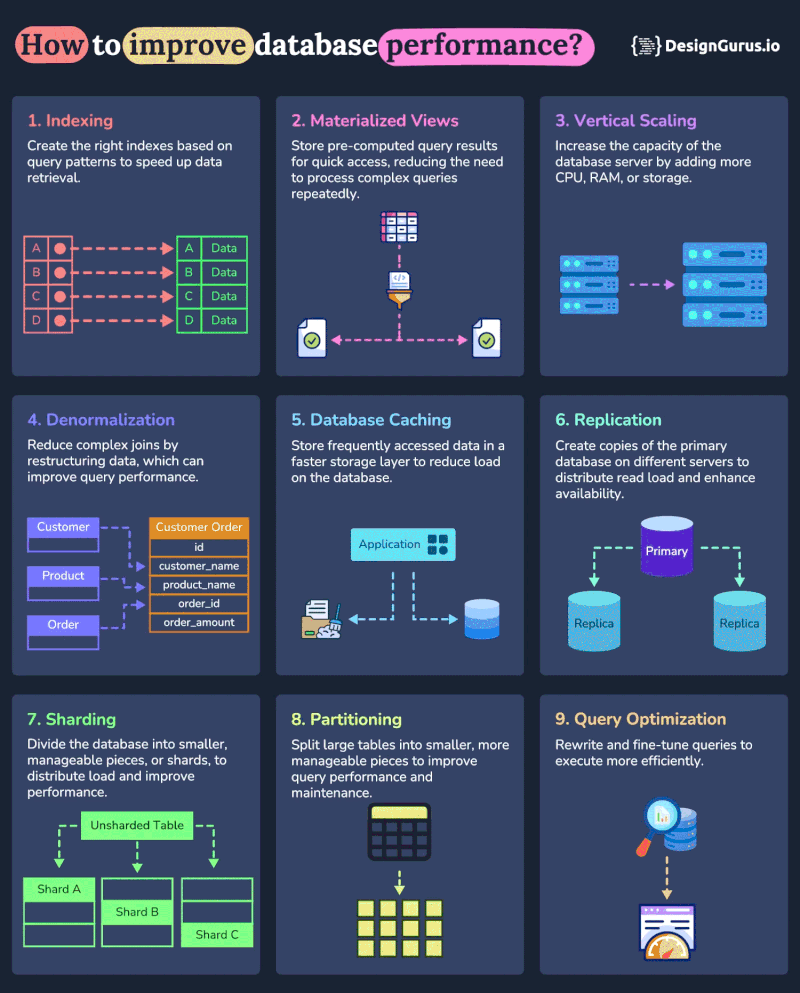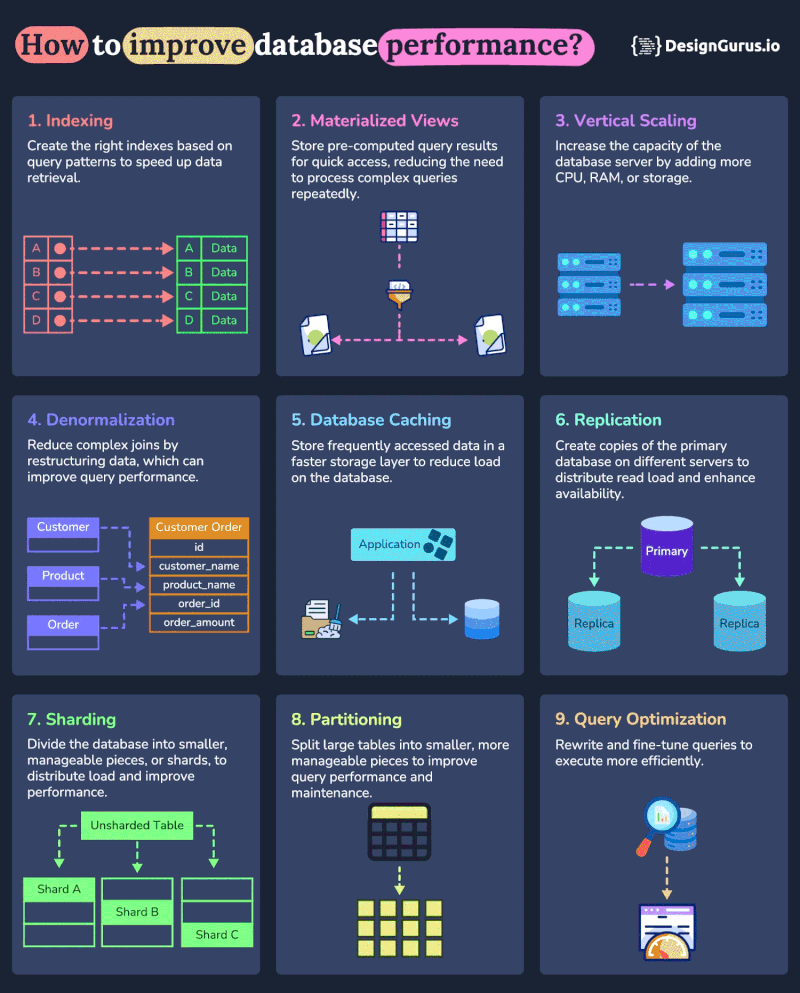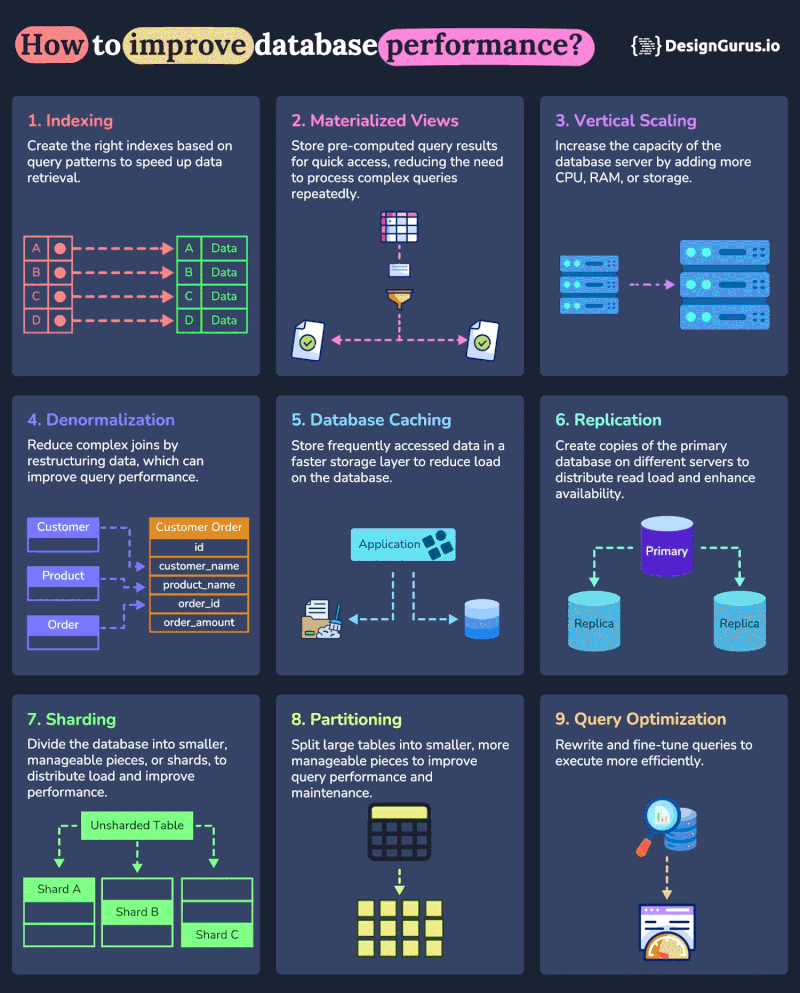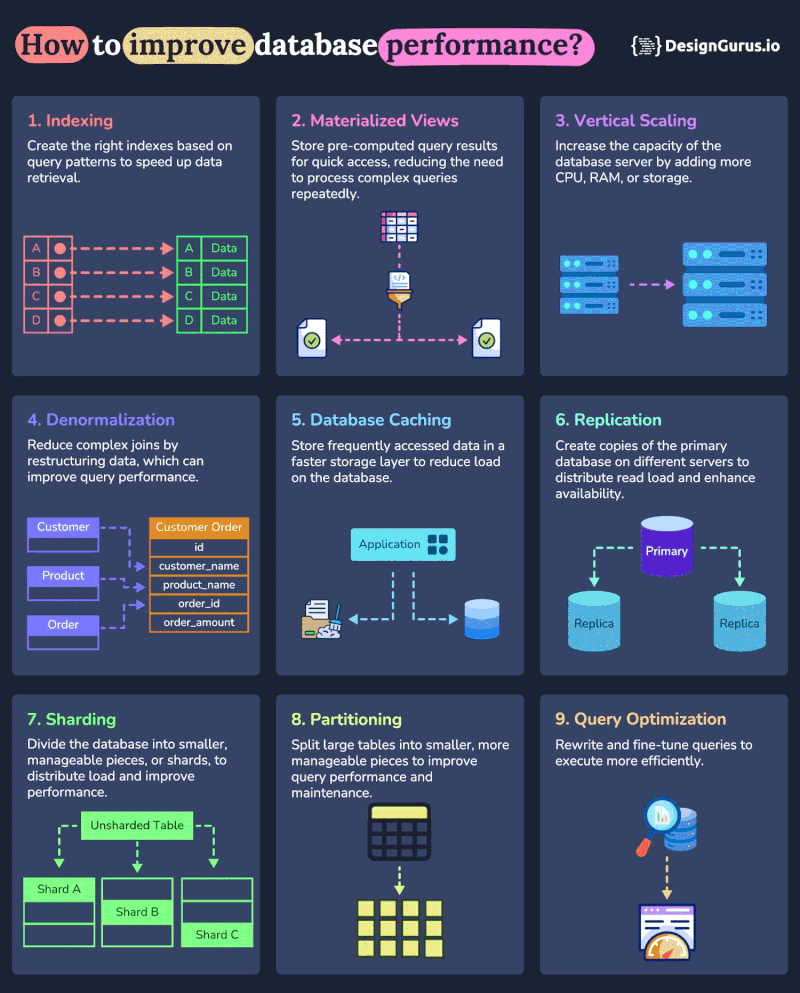
1. Indexing
Database Indexes are like lookup tables for your database.
By creating indexes on frequently queried columns (e.g., user ID, email, timestamps), you significantly reduce the time it takes to search and retrieve data.
✅ Use composite indexes for multi-column filtering and
EXPLAINplans to audit index usage.
Though, you should also be careful with how many index you create as more index means insert and update will become slower as your index needs to be adjusted after every insert or update.
Here is how index looks in database:
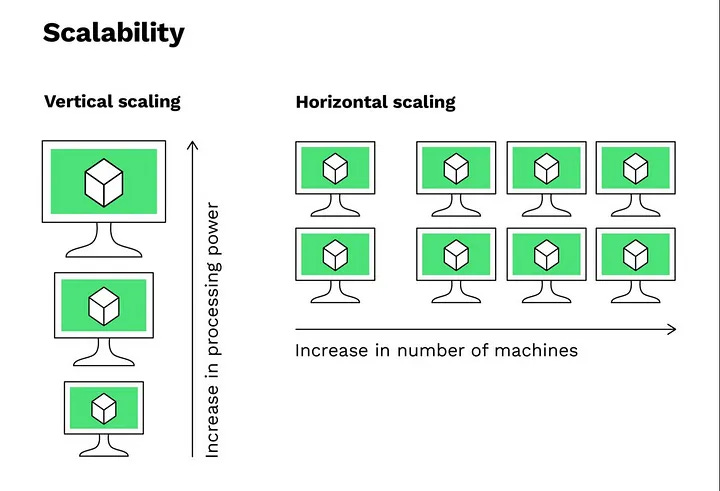
2. Vertical Scaling
The simplest way to scale you application is to upgrade your server — I mean add more CPU, more memory, faster disks. This technique is known as Vertical Scaling
This works well for short-term growth because you don’t need to setup additional server and install your application on them but eventually hits a ceiling.
✅ Best for early-stage apps where horizontal complexity isn’t justified yet.
If you already vertically scaled your app them it may be time for horizontal scaling.
3. Caching
Caching reduce database load by caching frequent reads in in-memory stores like Redis or Memcached.
This drastically improves performance for read-heavy systems (e.g., user profiles, product listings).
✅ Implement with sensible TTLs and fallback strategies.
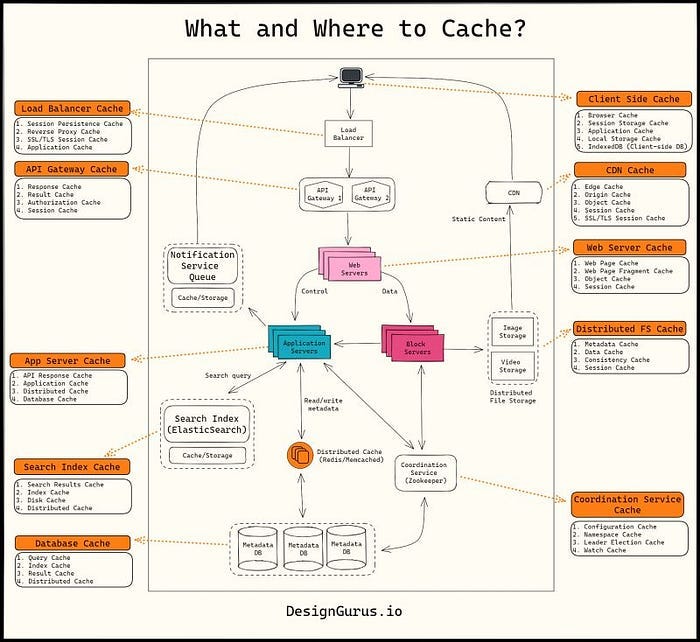
Here is a quick guide from DesignGurus.io, one of the popular resource for System Design prep, of what to cache and where to cache
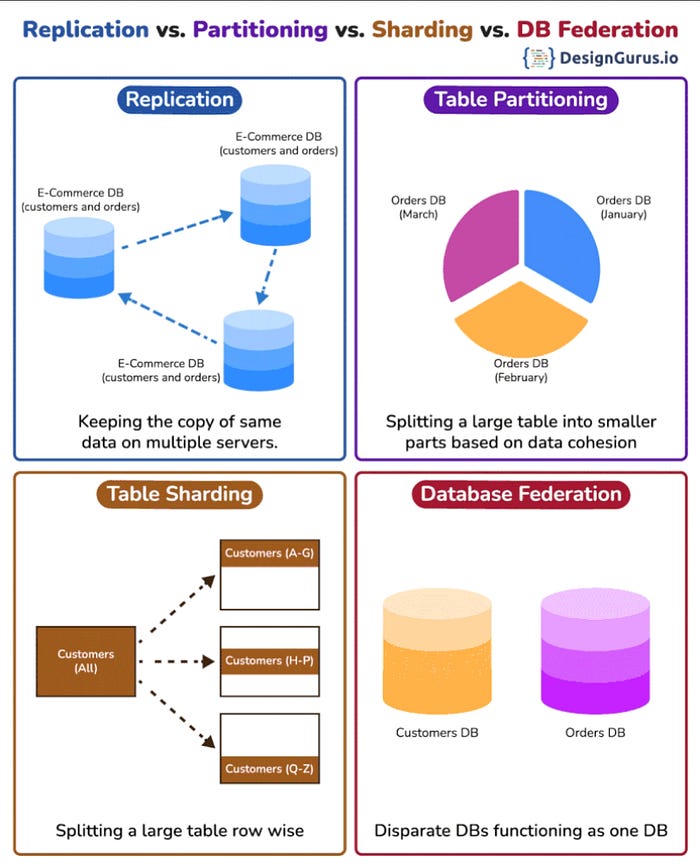
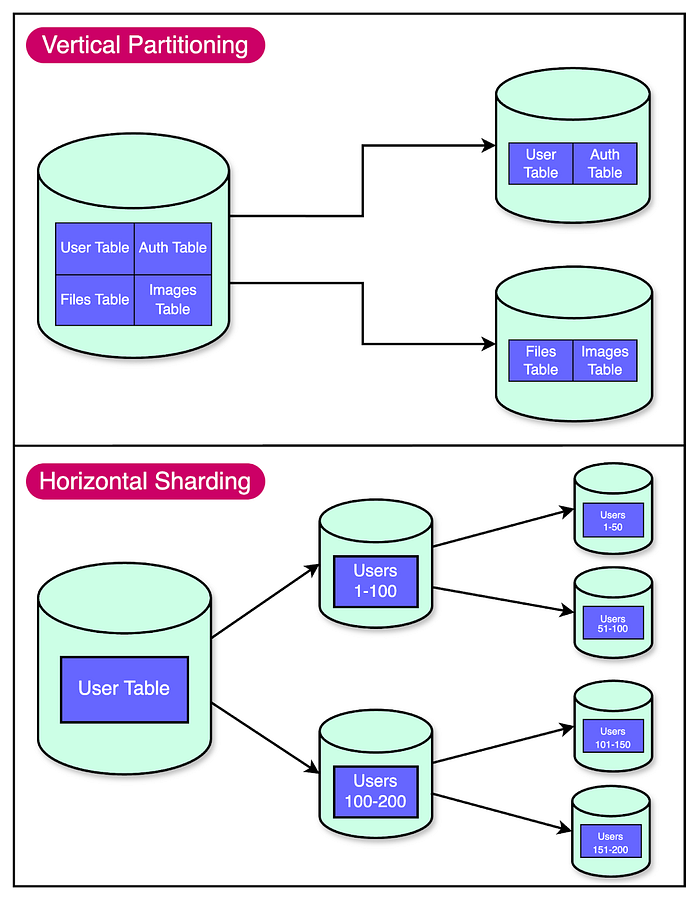
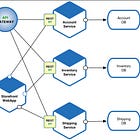
4. Sharding
This is another technique to scale your database and I have talked about it earlier also.
Sharding splits your database into smaller, independent chunks, often by user ID, region, or time.
Each shard lives on a different server — enabling horizontal scaling.
✅ Critical for systems with huge datasets and global users.
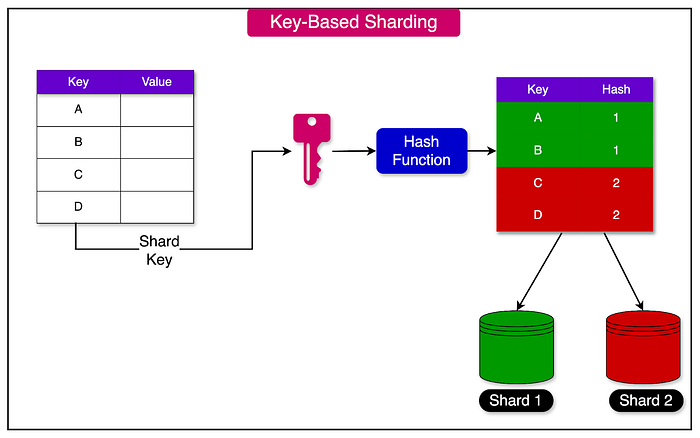
Here is an example of key base sharding from ByteByteGo, another popular website for learning System Design concepts. It's also one of my favorite place to prepare for coding interviews. They are also offering 50% discount now on their lifetime plan which I just grabbed as its essential every time you look for job.
5. Replication
With replication, you maintain multiple copies of the same data across different nodes.
This allows you to offload read queries to replicas and ensure high availability.
✅ Use synchronous replication for consistency or asynchronous for speed.
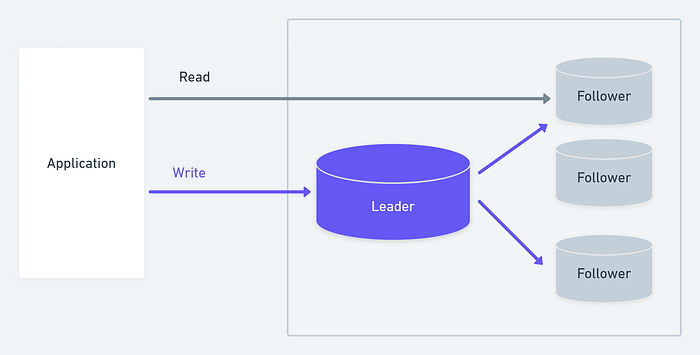
Here is an example of database replication strategies from Exponent, another great resource for System design interviews, particularly for mock interviews.
6. Query Optimization
Slow queries kill scalability. You can use tools like EXPLAIN, query plans, and index hints to fine-tune performance.
You should also avoid SELECT *, reduce joins, and fetch only the data you need.
✅ Prioritize N+1 fixes and pagination strategies.
You know what, you can use AI tools like ChatGPT and GitHub Copilot to optimize your query. It works well but don’t forget to test them.
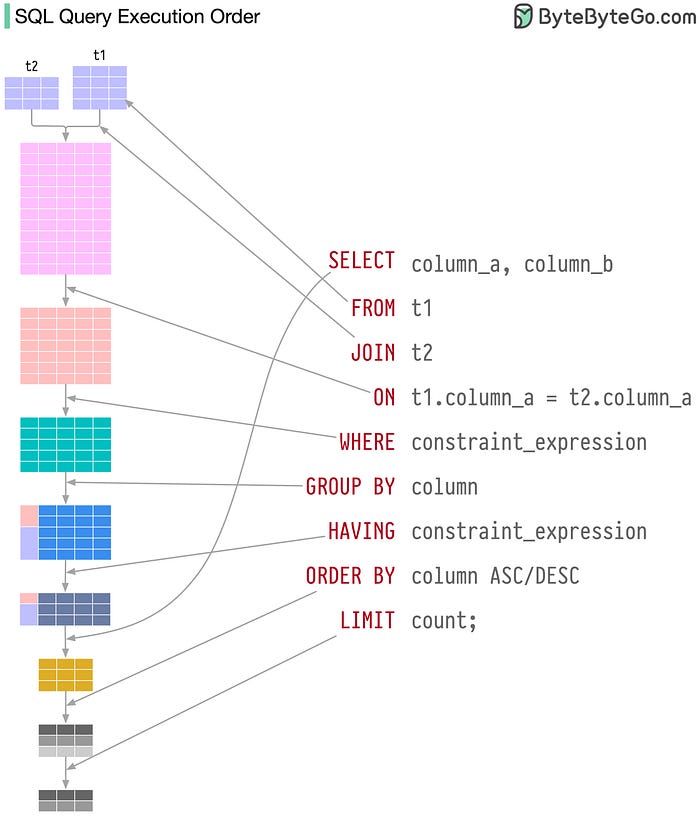
It’s also important to know the SQL Query execution order before you try to optimize them and this diagram from ByteByteGo is a great resource to learn that
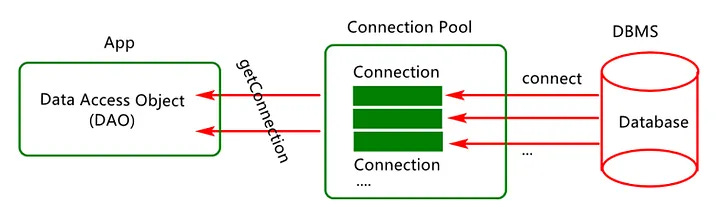
7. Connection Pooling
Database connections are expensive and it also takes time to create them.
With connection pooling, you reuse existing connections instead of constantly opening new ones — reducing latency and server load.
✅ Use libraries like HikariCP (Java), PgBouncer (Postgres), or SQLAlchemy pooling (Python).
8. Vertical Partitioning
You can also split wide tables into smaller ones based on related columns.
This helps reduce I/O and memory usage, especially for large blob-heavy tables.
✅ Ideal when some columns are rarely accessed (e.g., archived metadata).
And, here is a nice diagram from ByteByteGo showing both horizontal sharding and vertical partitioning of database
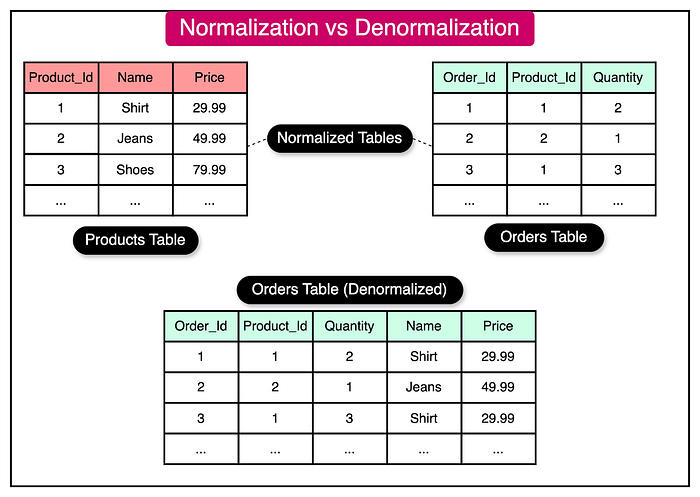
9. Denormalization
You might have heard about how you can use normalization to reduce duplication in database but did you know about Denormilization?
Well, Denormalization sacrifices storage space to eliminate complex joins.
By duplicating some data across tables, you can speed up reads dramatically.
✅ Common in analytics dashboards and NoSQL-style architectures.
Here is a nice diagram from ByteByteGo which shows the difference between normalization and denormalization
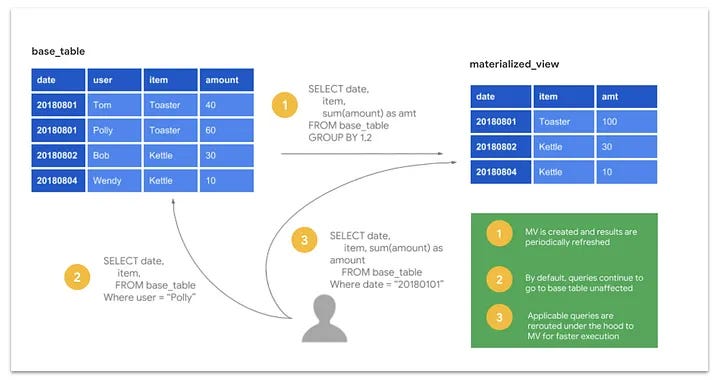
10. Materialized Views
Instead of re-running complex joins and aggregations, pre-compute the results and store them in a table.
Materialized views reduce load and response time for expensive queries.
✅ Refresh periodically or on-demand for near real-time accuracy.
Here is how Materialized Views looks in BigQuery
Final Thoughts
That’s all about the 10 essential techniques for database scaling and performance improvement. Scaling databases isn’t a one-size-fits-all problem. It’s about using the right combination of techniques based on your application’s current scale, growth trajectory, and workload patterns.
Start simple — cache aggressively, index wisely, and tune your queries. As you grow, look at sharding, replication, and eventually redesigning your architecture around horizontal scale.
Understanding these techniques is a key skill for any backend engineer, SRE, or database architect. Master them, and your systems will stay fast, resilient, and future-proof.
And here is a nice diagram from DesignGurus.io on how you can use these techniques to improve performance of your database:
Other System Design and AI articles you may like