Designing Microservices Systems: 10 Patterns That Actually Work
Microservices architecture are mess without these patterns
FAANG Interview coming up? Join ByteByteGo now for a structured preparation. They are also offering a rare 50% discount now on their lifetime plan
Hello guys, if you are using Microservice architecture and want to learn about different Microservice design patterns and principles to better architect your application then you have come to the right place.
Earlier, I have talked about Monolith vs Microservice architecture, and in this article, I am going to share the essential Microservice design principle and patterns.
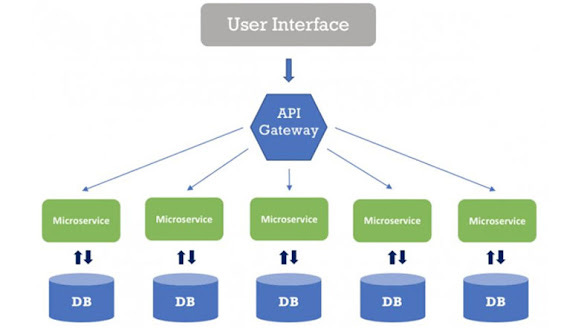
We will cover patterns like Event Sourcing, Circuit Breaker, SAGA, CQRS, Strangler, Database per Microservices, Backend for Frontend (BFF), Service Discovery, and API Gateway and principles like Scalability, Flexibility, Resiliency, etc.
📣Coursera 50% OFF (Sponsored)
Level up your Java and Microservices skills with Coursera Plus at 50% off, get a full year for just $199 (normally $399). The offer ends Feb 2nd, making this a great time to start learning AI, Machine Learning, and other in-demand tech skills from top universities and companies.
When you developing an enterprise application, it is good to move with micro-services rather than move with a monolithic architecture.
While there are cases where you would like to go with monolithic architecture like for low latency applications, but in most cases where you want to run your Java application in the cloud, Microservice architecture offers a better solution.
So let’s have a quick look into what is microservices and it’s use cases and design patterns for micro-services.
What is Microservice Architecture?
The microservice architecture is structured on the business domain and it’s a collection of small autonomous services. In a microservice architecture, all the components are self-contained and wrap up around a single business capability.